Plate & Frame Heat Exchangers Explained
This article was written by Jennifer Kaelin, an expert at Thermaxx Jackets
What is a plate and frame heat exchanger?
The concept behind a heat exchanger is the use of pipes or other containment vessels to heat or cool one fluid by transferring heat between it and another fluid. In most cases, the exchanger consists of a coiled pipe containing one fluid that passes through a chamber containing another fluid. The walls of the pipe are usually made of metal, or another substance with a high thermal conductivity, to facilitate the interchange, whereas the outer casing of the larger chamber is made of a plastic or coated with thermal insulation, to discourage heat from escaping from the exchanger.
An Uninsulated Plate & Frame Heat Exchanger
Most of the heat exchangers used in industry are shell and tube, air cooled, or plate and frame. Typically, plate and frame heat exchangers are used for liquid-liquid exchange at low to medium pressures. However, gasket-free plate and frame heat exchangers can safely operate at high temperatures and pressures. Plate and frame heat exchangers offer flexibility because plates can be either added or compressed for each different situation.
Plate and frame heat exchangers are made of corrugated plates on a frame. This design creates high turbulence and high wall shear stress, both of which lead to a high heat transfer coefficient and a high fouling resistance. Fluids travel within the heat exchanger. The two streams flow counter currently. The hot fluid flows down one plate while the cold fluid flows up the other plate.
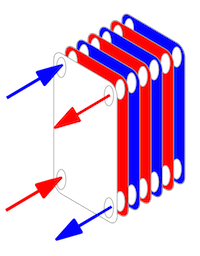 Gaskets ensure that the cold fluid and the hot fluid don't mix. Alternatives to the traditional gasket seal include brazing and laser welding.
Gaskets ensure that the cold fluid and the hot fluid don't mix. Alternatives to the traditional gasket seal include brazing and laser welding.
The plates are stacked in an alternating manner to cause the counter current flow. Multiple plates are clamped together and sealed at the edges. The design allows for the two fluids to flow in alternate directions and not be mixed. However, heat can be transferred from one medium to the other through the plates.
Because gasketed plate and frame exchangers are easy to clean, they are especially useful for food and pharmaceutical processing, where high degrees of sanitation are required.
Types of plate heat exchangers
There are four main types of plate heat exchangers:
- Gasketed plate heat exchangers use high quality gaskets and design to seal plates together and protect against leaks. Plates can easily be removed for cleaning, expansion, or replacing purposes, drastically reducing maintenance costs.
- Brazed Plate heat exchangers are used in many industrial and refrigeration applications. Due to stainless steel plate composition with copper brazing, they are highly resistant to corrosion. Brazed Plate heat exchangers are efficient and compact, making them an excellent economic choice.
- Welded plate heat exchangers are similar to Gasketed plate heat exchangers, but instead the plates are welded together. They are extremely durable, and are ideal for transferring fluids with high temperatures or corrosive materials. Since the plates are welded together, mechanical cleaning of plates is not an option as with plate and frame heat exchangers.
- Semi-Welded plate heat exchangers feature a mixture of welded and gasketed plates. They contain pairs of two plates welded together which are then gasketed to other pairs, therefore one fluid path is welded and the other fluid path is gasketed. This results in a plate heat exchanger that is easy to service on one side and able to transfer more intense fluids on the other. Semi-Welded heat exchangers are perfect for transferring expensive materials since they have a very low risk of fluid loss.
API Schmidt-Bretten offers all four types. Each type is suited for a number of applications in various industrial fields.
Alternatives to plate and frame heat exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are not the best choice for all applications. In situations where there is an extreme temperature difference between two fluids, it is generally more cost efficient to use a Shell & Tube heat exchanger . In a Plate heat exchanger, there can be a high pressure loss due to the large amount of turbulence created by the narrow flow channels. Applications which require a low pressure loss may want to consider a Shell & Tube heat exchanger as well.
 Shell and tube exchangers consist of a number of tubes held within a shell. Heat transfer takes place between one fluid flowing through the tubes whilst another fluid flows over the tubes in the shell.
Shell and tube exchangers consist of a number of tubes held within a shell. Heat transfer takes place between one fluid flowing through the tubes whilst another fluid flows over the tubes in the shell.
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers are limited in high fluid temperatures, by the temperature limitations of the gasket. Despite these limitations, Plate heat exchangers are the most efficient choice for a wide variety of applications.
Plate heat exchangers are now common and very small brazed versions are used in the hot-water sections of millions of combination boilers. The high heat transfer efficiency for such a small physical size has increased the domestic hot water flow rate of combination boilers. The small plate heat exchanger has made a great impact in domestic heating and hot water. Larger commercial versions use gaskets between the plates, whereas smaller versions tend to be brazed.
Advantages and disadvantages of plate and frame heat exchangers
A plate & frame heat exchanger has the following advantages over the widely used shell and tube heat exchangers:
- High value for overall heat transfer coefficient, for the same two fluids, a flat plate heat exchanger typically has a U value much higher than either a shell and tube heat exchanger or a spiral heat exchanger.
- Compact design - The combination of high value for the overall heat transfer coefficient and the general compact configuration of the flat plate heat exchanger lead to its ability to have the same thermal capacity as a shell and tube heat exchanger as much as five times its size
- Easy maintenance and cleaning - The fact that a plate and frame heat exchanger can be taken apart as discussed in the previous section, allows for easy cleaning and maintenance. A plate and frame heat exchanger can be designed to allow for easy addition or removal of plates to expand or reduce its heat transfer capacity.
- Temperature control - A flat plate heat exchanger works well with small temperature differences between the hot fluid and the cold fluid.
Plate & frame heat exchangers also has some disadvantages in comparison with other types of heat exchangers as follows:
- Potential for leakage - Although plate and frame heat exchangers are designed to allow the plates and the gaskets between them to be firmly clamped together, there is still a greater potential for leakage than with either shell and tube or spiral heat exchangers.
- Higher pressure drop - The narrow passageways for fluid flow, which lead to a high overall heat transfer coefficient, also lead to a higher pressure drop, and thus a higher cost for pumping, than shell and tube heat exchangers.
- Not good for large fluid temperature differences - A flat plate heat exchanger does not work as well as a shell and tube heat exchanger for cases where there is a large temperature difference between the two fluids.
- Doesn't work well with very high fluid temperatures - The gaskets may impose temperature limitations for plate and frame heat exchangers.
Insulating plate and frame heat exchangers
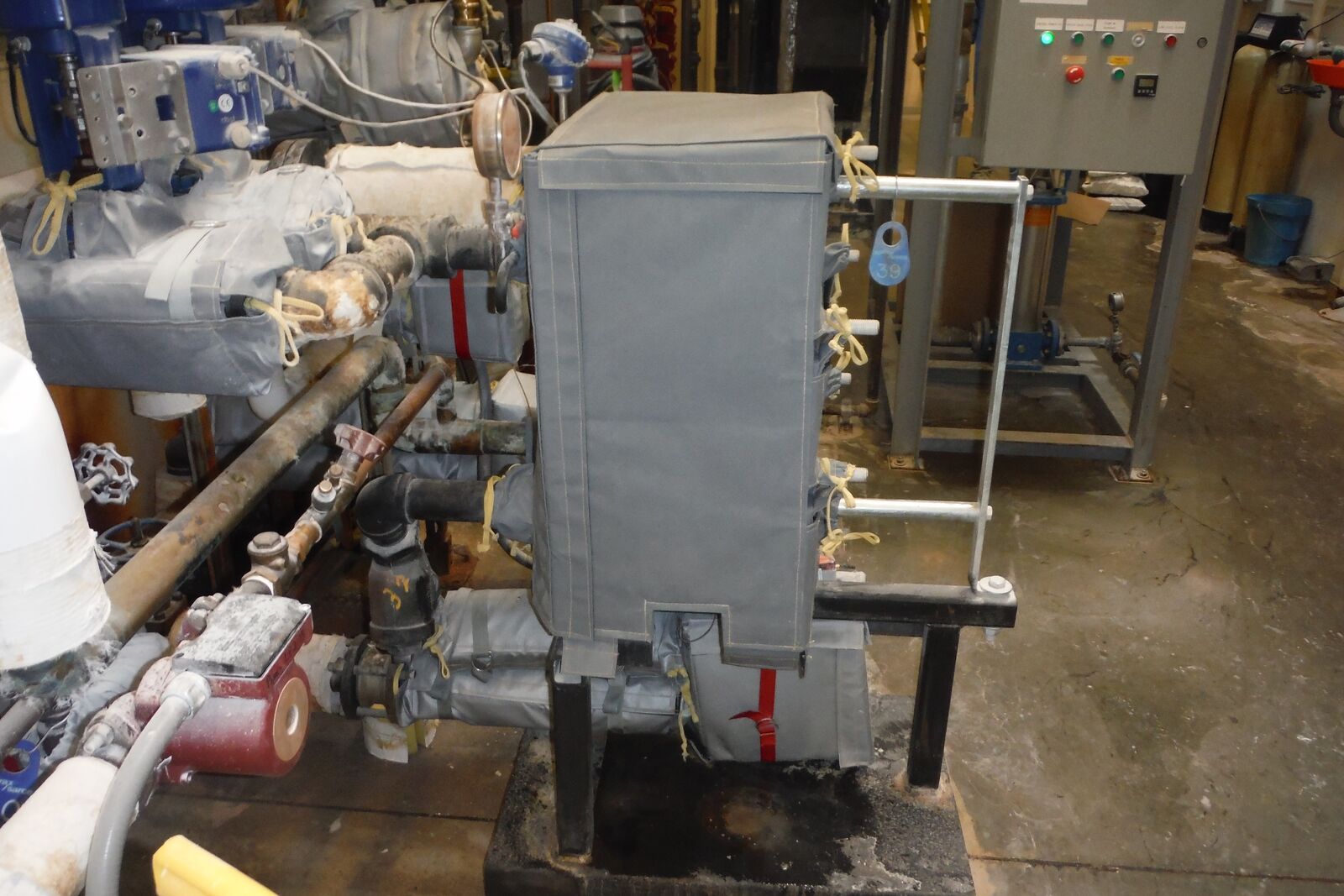
Heat exchangers must be adequately insulated to reduce heat losses. Because inspection and maintenance of heat exchangers is routine, stay-in-place insulation is not practical. Generally, heat exchanger experiences touch temperatures that differ from the ambient temperature, valuable heat is likely radiating away. In the cases of larger heat exchangers or facilities with multiple units, the amount of energy loss can be substantial.
Insulation coatings are a possible solution however it has to be reapplied each time maintenance is performed which is costly & labor intensive. Custom fit removable and reusable insulation is the most economic & efficient way to insulate heat exchangers allowing for easy on & off application as maintenance is required.
Plate & Frame Heat Exchanger Insulated by Thermaxx Jackets
Learn more about Thermaxx Insulation Jackets for Heat Exchangers
Read a case study featuring a plate and frame heat exchanger insulation project
Categories
- removable insulation
- thermaxx jackets
- energy savings
- savings
- energy efficiency
- safety
- pipe insulation
- energy
- case study
- insulation materials
- thermal insulation
- heat loss survey
- heat loss
- energy loss
- hot insulation
- fiberglass
- installation
- steam
- New York
- custom insulation
- NYC Case Study
- boiler
- university
- Connecticut
- reusable insulation







